Emotional misinformation spreading
Complexity Science Hub Vienna & University of Vienna
Slides: hannahmetzler.eu/emomis_update_2024
2024-04-09
The Project
Introduction

- Emotions attract attention & increase sharing
- Beliefs are shaped by our social identity
- Group & emotion dynamics are central on social media
- Existing interventions focus on accuracy
Research questions
Observational social media analyses of emotional dynamics around news
Emotion regulation interventions 
 Agent-based modelling: network & algorithms
Agent-based modelling: network & algorithms
Results & Highlights (Part I)
Do fake news elicit emotions?
- COVID-19 news headlines
- Austria 2021
- Mood & response
- Response:
- More anger
- Less joy
Lühring*, Shetty*, Koschmieder, Waldherr, Garcia & Metzler (2023), PsyarXiv.
Do emotions increase susceptibility?
- Higher anger in people good & bad at recognizing false news
- Angry responses because most people recognize false news
- Emotions arise when information contradicts existing beliefs
Lühring*, Shetty*, Koschmieder, Waldherr, Garcia & Metzler (2023), PsyarXiv.
Theory: Change of problem understanding
- Emotions are functional
- Humans are not gullible: motivated belief vs. manipulation
- Misinformation as symptom of real-world societal problems
- Motivated partisan minority shares misinformation
- Majority: uninformed, little news interest & silent
Results & Highlights (Part II)
Measuring misinformation: NewsGuard
Expert ratings of news sources on 9 journalistic quality criteria
- Trustworthiness score per source
- In-depth analysis
- Increasing inclusion of low-trustworthy news
- Includes German sources since 2019
Lühring, Shetty, Lazzaroni, Lasser & Metzler (in preparation).
Emotions around news on Twitter
Discussion threads below tweets linking to news sources
- German speaking
- Emotions:
Machine Learning
Lühring, Hapig, Shetty, Garcia, Waldherr & Metzler (in prep.)
Emotions depend on news trustworthiness
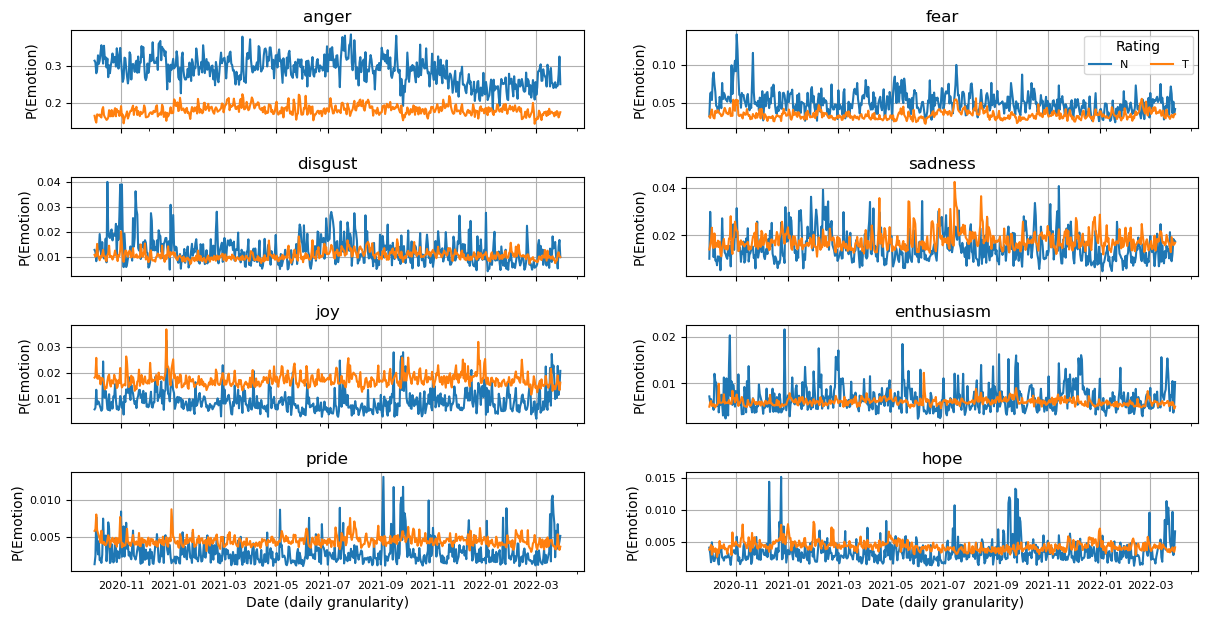
Low-trustworthy news: more anger & less joy (preliminary!)
N = Non-trustworthy T = Trustworthy
Intervention effect on trust & sympathy
Algorithm effects on news trustworthiness
Agent-based model of US politicians’ retweeting behavior
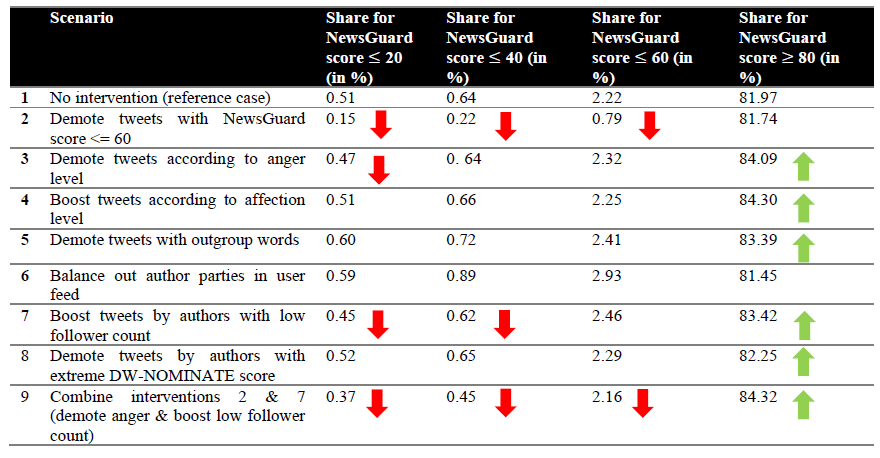
Shetty*, Simmerdinger*, Lühring, Garcia, Walherr & Metzler (in prep.)
Other highlights
- 3 supervised internships + 2 Master theses
- Presentations at leading conferences: ICA Toronto 2023, MISDOOM Amsterdam 2023, SPSP 2022 (online), …
- EMOMIS Video for the Digital Humanism series
- Chapter in a public report on climate misinformation
- Media mentions (APA, DerStandard, Kurier, Science.ORF, FM4 news, Woman Balance…)
Upcoming outreach highlights
- Upcoming talks
- klimaaktiv (Bundesministerium für Klimaschutz, May)
- Volkshochschule (September)
- Upcoming media highlights
- ORF documentary
- DERSTANDARD Podcast
- Article in Spektrum der Wissenschaften
Thank you!
- Project website: hannahmetzler.eu/emomis
- Preprint: Emotions in misinformation studies.
- Paper: Social drivers & algorithmic mechanisms on digital media


Appendix
COVID-misinformation items
- Actual true & false COVID-19 headlines
- From fact-checking websites & mainstream news sources
- Accuracy ratings
Social identity intervention